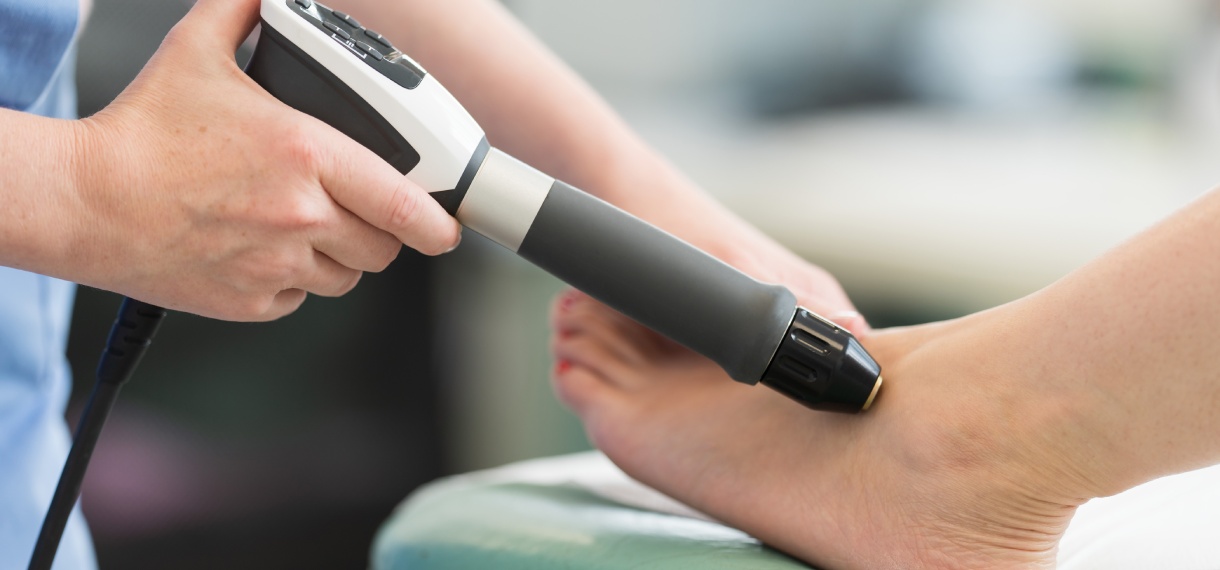
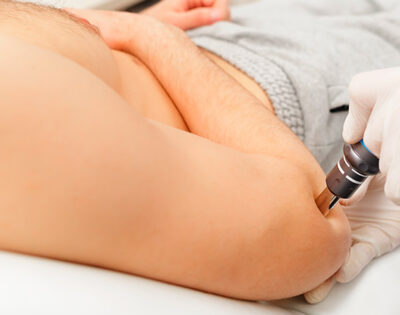
Shockwave therapy is a cutting-edge, non-invasive treatment that harnesses the power of acoustic waves to address a variety of musculoskeletal conditions, provide pain relief, and promote tissue regeneration. This innovative approach has been gaining traction in the medical community and among patients seeking alternatives to surgery and long-term medication use.
- Definition: A non-invasive treatment using high-energy acoustic waves
- Primary Uses: Treating musculoskeletal conditions, alleviating chronic pain, and stimulating tissue repair
- Growing Popularity: Offers an effective alternative to invasive procedures, with minimal side effects
Types of Shockwave Therapy
Focused Shockwave Therapy (FSWT)
FSWT utilizes high-energy waves targeted at specific areas, allowing for deeper penetration into tissues.
- Energy Delivery: Concentrated acoustic waves focus on a precise point within the tissue
- Depth: Can reach up to 12 cm beneath the skin surface
- Best for: Chronic conditions like plantar fasciitis, calcific tendinitis, and non-union fractures
Radial Shockwave Therapy (RSWT)
RSWT employs lower energy waves that are dispersed over a wider area, ideal for treating superficial tissues.
- Energy Delivery: Radial pressure waves spread in a fan-like pattern
- Depth: Typically effective up to 3-4 cm beneath the skin surface
- Best for: Myofascial pain, trigger points, and surface-level soft tissue disorders
Biological Mechanisms of Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave therapy’s effectiveness stems from its ability to trigger several biological responses:
Neovascularization
- Process: Stimulates the formation of new blood vessels in the treated area
- Benefit: Improves blood circulation, enhancing oxygen and nutrient delivery
- Result: Accelerated healing and tissue regeneration
Pain Reduction
- Mechanism: Triggers the release of endorphins and other pain-inhibiting substances
- Effect: Interrupts pain signals to the brain, providing immediate relief
- Long-term benefit: Modulates pain perception, offering lasting comfort
Tissue Regeneration
- Cellular level: Activates dormant stem cells in the treated area
- Growth factors: Increases production of growth factors that promote healing
- Tissue quality: Breaks down scar tissue and calcifications, improving overall tissue health
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
- Mediators: Reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines
- Swelling: Helps in decreasing localized inflammation and edema
- Healing: Accelerates the transition from inflammation to proliferation phase of healing
Shockwave Therapy Procedure
Preparation
- Assessment: Thorough patient evaluation and precise diagnosis of the condition
- Education: Detailed explanation of the procedure, expected sensations, and potential benefits
- Setup: Application of coupling gel to ensure optimal acoustic wave transmission
Treatment
- Application: Delivery of shockwaves through a handheld device placed on the skin
- Intensity: Gradual increase in wave intensity, tailored to patient comfort and condition
- Duration: Typically 2000-3000 pulses per session, lasting about 15-20 minutes
Post-Treatment
- Immediate effects: Possible mild discomfort or redness, usually subsiding within hours
- Recovery: No downtime required; patients can usually return to normal activities immediately
- Follow-up: Subsequent appointments to assess progress and adjust treatment parameters if needed
Advantages of Shockwave Therapy
- Non-invasive: Avoids the risks associated with surgery and general anesthesia
- Minimal side effects: Reduces the likelihood of complications and adverse reactions
- Outpatient procedure: Convenient, typically requiring no hospitalization
- Customizable: Treatment parameters can be adjusted based on individual patient needs
- Versatile: Effective for various musculoskeletal and chronic pain conditions
- Natural healing: Stimulates the body’s own regenerative processes without medication
Potential Applications of Shockwave Therapy
Musculoskeletal Conditions
- Tendinopathies: Effective for conditions like tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, and Achilles tendinitis
- Plantar fasciitis: Particularly useful for chronic cases resistant to conservative treatments
- Calcific tendinitis: Helps break down calcium deposits in tendons, especially in the shoulder
- Muscle injuries: Aids in the recovery of muscle strains, tears, and chronic muscle pain
Other Conditions
- Chronic pain syndromes: Beneficial for conditions like fibromyalgia and myofascial pain syndrome
- Bone healing: Promotes healing in delayed union and non-union fractures
- Erectile dysfunction: Emerging evidence supports its use in improving blood flow and tissue regeneration
Conclusion
Shockwave therapy represents a significant advancement in the treatment of various musculoskeletal and chronic pain conditions. By harnessing the body’s natural healing processes through acoustic wave stimulation, this therapy offers a safe, effective, and non-invasive alternative to traditional treatments. As research continues to uncover new applications and refine existing protocols, shockwave therapy stands poised to revolutionize the field of regenerative medicine and pain management, providing hope for patients seeking alternatives to surgery and long-term medication use.